Company
ServiceNSW
Year
2021
Type
Design System
Team
Srishti, Another Designer
Review screen
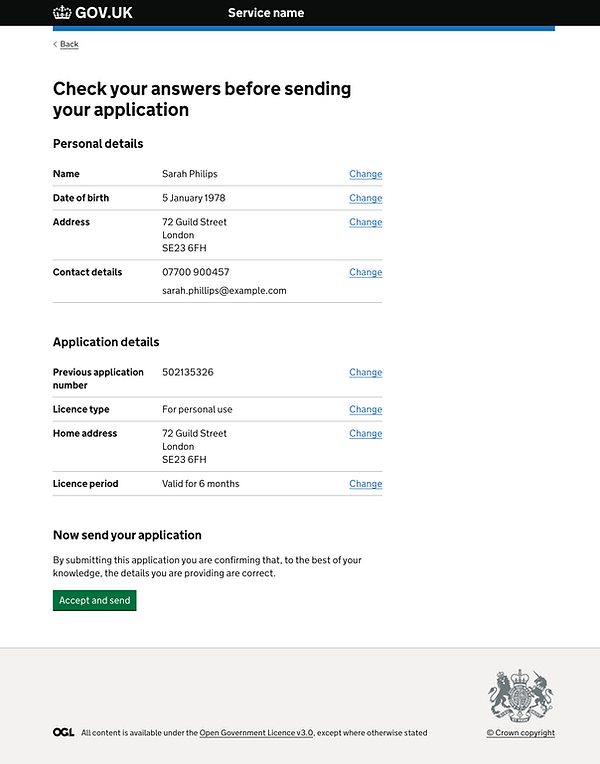
A review screen allows customers to check their answers before submitting information to a service.
GEL reached a point where we were transitioning from patterns to creating a page in our design system. We faced a challenge with the review screen, which is the last step before confirmation. It's where users get to double-check all their answers before hitting submit. This marked our first page design for SNSW.
AIM
To design and integrate a review screen in the SNSW design system, enabling users to double-check their answers before submission.
REQUIREMENT
Ensure that the GEL provides a clear and intuitive review screen where users can easily recognise they are on the page to review and edit their information before submitting a form.
The design should offer guidance and maintain flexibility in its structure, allowing different teams to use it efficiently across various services.
DISCOVERY
Internal
Gathered and analysed information to gain insights and understanding about various designs of review screens within the SNSW.
Collected and analyzed existing review screen designs currently utilized by various product teams in their transactions and products

External research and best practices



Observations
After conducting both internal and external reviews, here are some key observations from the existing designs.
Observation 1

Inconsistent content/copy widths
Recommendation -
Utilise 8 columns for copy to help with readability
Secondary research -
Atlassian recommends that line length does not reach more than 100 characters per line, to aid with readability
Observation 2

Personal details section sometimes appears in a blue box, however this is not consistent across the various internal example
Recommendation -
Utilise a visual styling, such as the blue box, to indicate the personal details is not editable within the application flow and include a message like the below to advise users how change their details.
Observation 3

inconsistent bolding of question and answer in internal examples.
Recommendation -
Bold the value to help users easily scan their answers. Often questions in applications can be longer than the value, so it can appear quite heavy when the question is bolded (refer to example 2)
Observation 4

inconsistent line spacing of content in internal examples.
Recommendation -
Follow GEL spacing guidelines and ensure similar/related content is closer together
Observation 5

*What we know from testing - users often skip over notification banners and do not read them. If we do use them, use them sparingly or display after an interaction to make users more likely to read them.
notification banners are inconsistently placed on page. Some designs have two banners at the top which is not ideal.
Recommendation -
include an info notification banner at the top if the application has a unique amount. Use a warning notifications sparingly, for example once the user selects the declaration checkbox and keep close to that content
Observation 6

declarations are inconsistent in headings, content and use of hyperlinks.
Recommendation -
keep the title as Declaration and simplify where possible. Separate links from checkbox options, so that the links are accessible
*Unknowns - do users read the declarations, is there a way to summarise the declarations instead of having a lot of checkboxes to tick
Observation 7

inconsistent ways of editing content and use of accordions
Recommendation -
display all content. Encourages users to scan the whole page before getting to the submit button.
*Assumption - accordians adds an additional interaction for users to review their information. Easy for users to skip.
Observation 8

some questions are quite long on the review screen
Recommendation -
consider rephasing questions as shorter statements
Pro - easier to scan
Con - involves more design input and potentially engineering effort as review questions will need to be individually crafted.
GOV.UK suggest - rephrase questions if you need to – for example, you do not need to label every individual line of an address, and you can rewrite long questions as shorter statements
DESIGN REQUIREMENT
-
Quick Review: Information should be laid out clearly to enable users to review their answers swiftly.
-
Seamless Edits: Ensure users can easily make changes to their answers while reviewing.
-
Organized Content: Group related or similar sections together for better clarity.
-
Effective Visual Hierarchy: Establish a clear visual hierarchy to guide users smoothly through the content.
-
Consistent Yet Flexible: Maintain a consistent design approach, while allowing flexibility to accommodate various transactions or applications.
-
Guided Interaction: Provide guidance tailored to different transactions or applications rather than enforcing a rigid pattern.

DESIGN OPTIONS
FINAL DESIGN
The final design offers a clear, structured layout that allows users to quickly review and edit their answers. Related sections are grouped for easy comprehension, and a strong visual hierarchy guides the user smoothly through the process. The design remains consistent yet flexible, accommodating various transactions with tailored guidance rather than a rigid pattern.
Structure of the page

1. The header shows the customer what step they’re up to.
2. The transaction summary is optional. This space is to relay critical information only.
3. Show the applicant’s details (optional) if there’s a chance of error, such as when applying on behalf of another person.
4. Each data group shows a list of all questions and answers within that group. It should be listed in the order the customer completed them and include an edit button at the end.
5. The edit button takes the customer to the corresponding section in the form so users can change their answers.
6.The declaration section is optional. This is where the customer can give consent legally to submitting their application. This section can be used to include terms and conditions, or other policies that need consent for from the customer.
7. The submit button sends the application for processing
ACCESIBILITY CONSIDERATION
-
If declaration checkbox is included, links taking the customer to another page or document shouldn’t be within the checkbox content area. This is because links within a checkbox can’t be interpreted by a screen reader. Refer to 6. Declaration in Anatomy on this page.
-
When there are multiple data groups in a review page, the edit button should describe the section the customer is editing. Refer WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4. – Link purpose.




